Intel® Upgrade Service - 0% Detection Rate *
Did you just download a file that has been digitally signed by Intel® Upgrade Service and wonder if the file is safe? If that's the case, please read on.
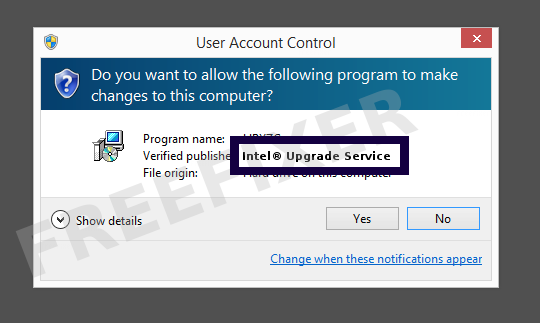
You will typically notice Intel® Upgrade Service when double-clicking to run the file. The publisher name is displayed as the "Verified publisher" in the UAC dialog as the screengrab shows:
You can view the additional details from the Intel® Upgrade Service digital signature with the following procedure:
- Open up Windows Explorer and locate the Intel® Upgrade Service file
- Right-click on the file and select Properties
- Click the Digital Signatures tab
- Click on the View Certificate button
Here's a screenshot of a file that has been signed by Intel® Upgrade Service:
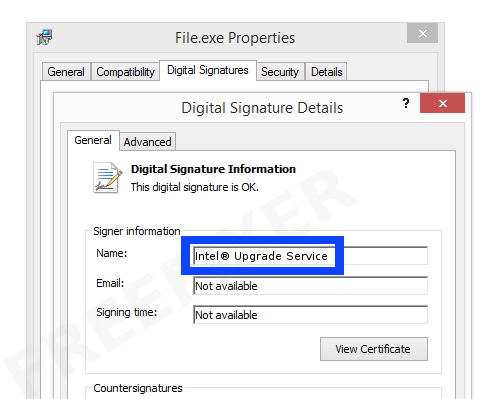
As you can see in the screenshot above, the Windows OS states that "This digital signature is OK". This means that the file has been published by Intel® Upgrade Service and that the file has not been tampered with.
If you click the View Certificate button shown in the screenshot above, you can see all the details of the certificate, such as when it was issued, who issued the certificate, how long it is valid, and so on. You can also see the address for Intel® Upgrade Service, such as the street name, city and country.
Intel External Basic Issuing CA 3A has issued the Intel® Upgrade Service certificates. You can also view the details of the issuer by clicking the View Certificate button shown in the screenshot above.
Intel® Upgrade Service Files
The following are the Intel® Upgrade Service files I have collected, thanks to the FreeFixer users.
| Detection Ratio | File Name |
|---|---|
| 0/46 | HeciServer.exe |
| 0/47 | HeciServer.exe |
| 0/48 | HeciServer.exe |
| 0/46 | HeciServer.exe |
| 0/47 | HeciServer.exe |
| 0/47 | heciserver.exe |
| 0/46 | HeciServer.exe |
| 0/47 | heciserver.exe |
| 0/55 | HeciServer.exe |
| 0/52 | HeciServer.exe |
* How the Detection Percentage is Calculated
The detection percentage is based on that I have gathered 481 scan results for the Intel® Upgrade Service files. 0 of these scan results came up with some sort of detection. You can review the full details of the scan results by examining the files listed above.
Analysis Details
The analysis is based on certificates with the following serial numbers:
- 217a8364000100006426